How Nurses Can Foster Trust with Younger Patients
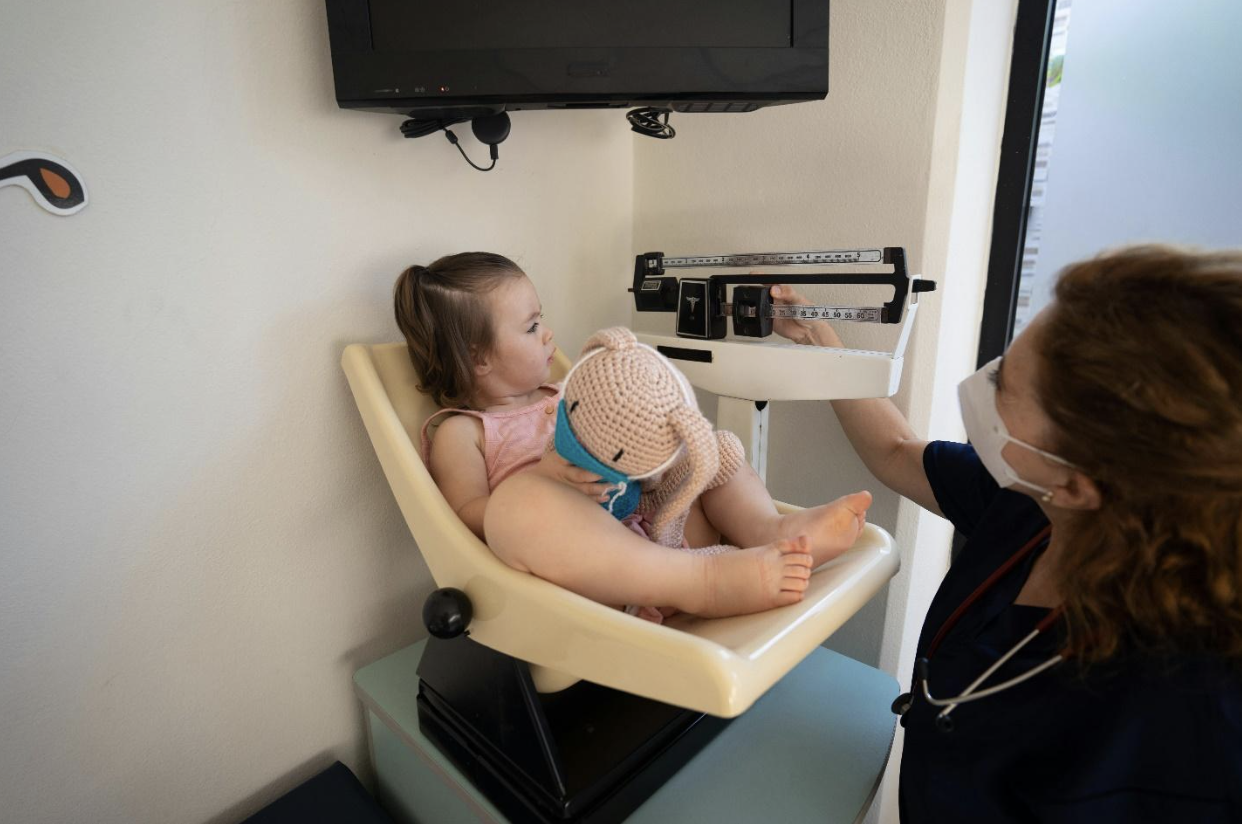
Building trust between nurses and younger patients is crucial for effective healthcare delivery. Children and teenagers often experience anxiety and fear in clinical settings, making it essential for nurses to establish a connection that reassures and comforts them.
Trust not only facilitates better communication but also encourages cooperation and adherence to medical advice. This article explores various strategies nurses can employ to foster trust with younger patients, ensuring a positive and supportive healthcare experience.
Understanding Developmental Stages
To build trust with younger patients, nurses must first understand the different developmental stages of childhood and adolescence. Communication needs and responses to medical interventions vary significantly between age groups, so tailoring interactions to the child’s developmental level is essential.
For infants and toddlers, nonverbal communication is key. Nurses should use gentle touch, maintain eye contact, and speak in soothing tones. These actions help create a sense of security and comfort. With preschool-aged children, using simple language and being honest about what to expect can reduce anxiety. Engaging them through stories or play can also be effective in gaining their trust.
School-aged children are more capable of understanding explanations about their care. Nurses should encourage questions and provide straightforward answers to help demystify medical procedures. For teenagers, respect their growing need for independence and privacy. Engage them in discussions about their health and listen actively to their concerns. This approach not only builds trust but also empowers them to take an active role in their healthcare.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Ongoing education is vital for nurses to enhance their skills in building trust with younger patients. Advanced training programs, such as an RN to BSN program, can significantly improve a nurse’s ability to communicate effectively with children and adolescents. These programs include specialized training that equips nurses with the knowledge and techniques needed to address the unique needs of pediatric patients. Moreover, professional development opportunities, such as workshops and seminars, keep nurses updated on the latest best practices in pediatric care.
By investing in continuing education, nurses can refine their approach to patient care, ensuring they are well-prepared to establish trust and provide high-quality care to younger patients.
Effective Communication Techniques
Effective communication is the cornerstone of building trust with younger patients. Nurses should use age-appropriate language and avoid medical jargon that might confuse or scare children. Simple, clear explanations help demystify medical procedures and reduce anxiety.
Active listening is another critical component. Nurses should listen attentively to what the child is saying and respond thoughtfully. This practice not only validates the child’s feelings but also shows that the nurse respects and cares about their perspective. Encouraging children to express their fears and concerns can help them feel more in control and less anxious.
Furthermore, using visual aids and demonstrations can make explanations more understandable for children. For example, showing a child how a blood pressure cuff works before using it can alleviate fear and build trust. Personalizing interactions by remembering the child’s name and interests can also make them feel valued and more comfortable.
Building a Safe and Comfortable Environment
Creating a safe and comfortable environment is crucial for fostering trust with younger patients. The physical setting of the healthcare facility can significantly impact a child’s experience. Child-friendly environments that include colorful decorations, toys, and activities can make the space feel less intimidating.
Nurses should strive to create a welcoming atmosphere where children feel safe. This can be achieved by maintaining a calm and friendly demeanor, using a gentle touch, and offering reassurance throughout the medical process. Allowing children to bring a favorite toy or blanket to appointments can also provide comfort and security.
Involving Parents and Guardians
Parents and guardians play a vital role in building trust between nurses and younger patients. Involving them in the care process helps reassure the child and provides emotional support. Nurses should communicate openly with parents, keeping them informed about their child’s condition and treatment plan.
Including parents in discussions about care decisions and encouraging them to ask questions fosters a collaborative approach. This involvement not only builds trust with the child but also with the parents, who are more likely to feel confident in the care their child is receiving.
Balancing the involvement of parents with the independence of older children is also important. For teenagers, who may prefer more privacy, nurses should respect their need for independence while still keeping parents informed and involved. This approach helps maintain trust with both the patient and their family.
Being Honest and Transparent
Honesty and transparency are fundamental in building trust with younger patients. Children and teenagers can often sense when they are not being told the whole truth, which can increase their anxiety and erode trust. Therefore, it is important for nurses to explain medical procedures and treatments in an age-appropriate manner without hiding critical information.
When discussing medical procedures, use simple language that a child can understand. Avoid medical jargon that can confuse or intimidate them. For instance, instead of saying, "We need to insert an intravenous catheter," say, "We need to put a small tube in your arm to give you medicine." Being upfront about what will happen helps demystify the process and reduces fear.
Moreover, it is essential to manage expectations by explaining what the child might feel during a procedure. If something might hurt, it is better to acknowledge it rather than promise that it won’t hurt at all. Providing this honesty, coupled with reassurance and support, helps children feel respected and involved in their care, which builds trust.
To Sum It Up
Building trust with younger patients is a critical aspect of nursing that requires empathy, effective communication, and a child-centered approach.
By focusing on these elements, nurses can create a positive and supportive environment that helps children feel safe and understood. This strong foundation of trust ultimately leads to more effective care and a better overall experience for young patients and their families.